Optimizing ingestion with commit lag configuration
note
Deprecated content
This page applies to QuestDB 6.5.5 and earlier versions. From QuestDB 6.6 onwards, the database adjusts relevant settings automatically and provides maximum ingestion speed.
The QuestDB commit lag configuration provides options to optimize data ingestion efficiency, when:
- ingesting data over InfluxDB Line Protocol (ILP), and
- receiving out-of-order (O3) data.
As of software version 6.0, QuestDB adds support for O3 data ingestion. The skew and latency of out-of-order data are likely to be relatively constant, so users may configure ingestion based on the characteristics of the data for optimum throughput.
This page explains the concept of commit lag and the way to configure it.
What is a commit lag?#
Most real-time O3 data patterns are caused by the delivery mechanism and hardware jitter, and therefore the timestamp distribution tends to be contained by some boundary.
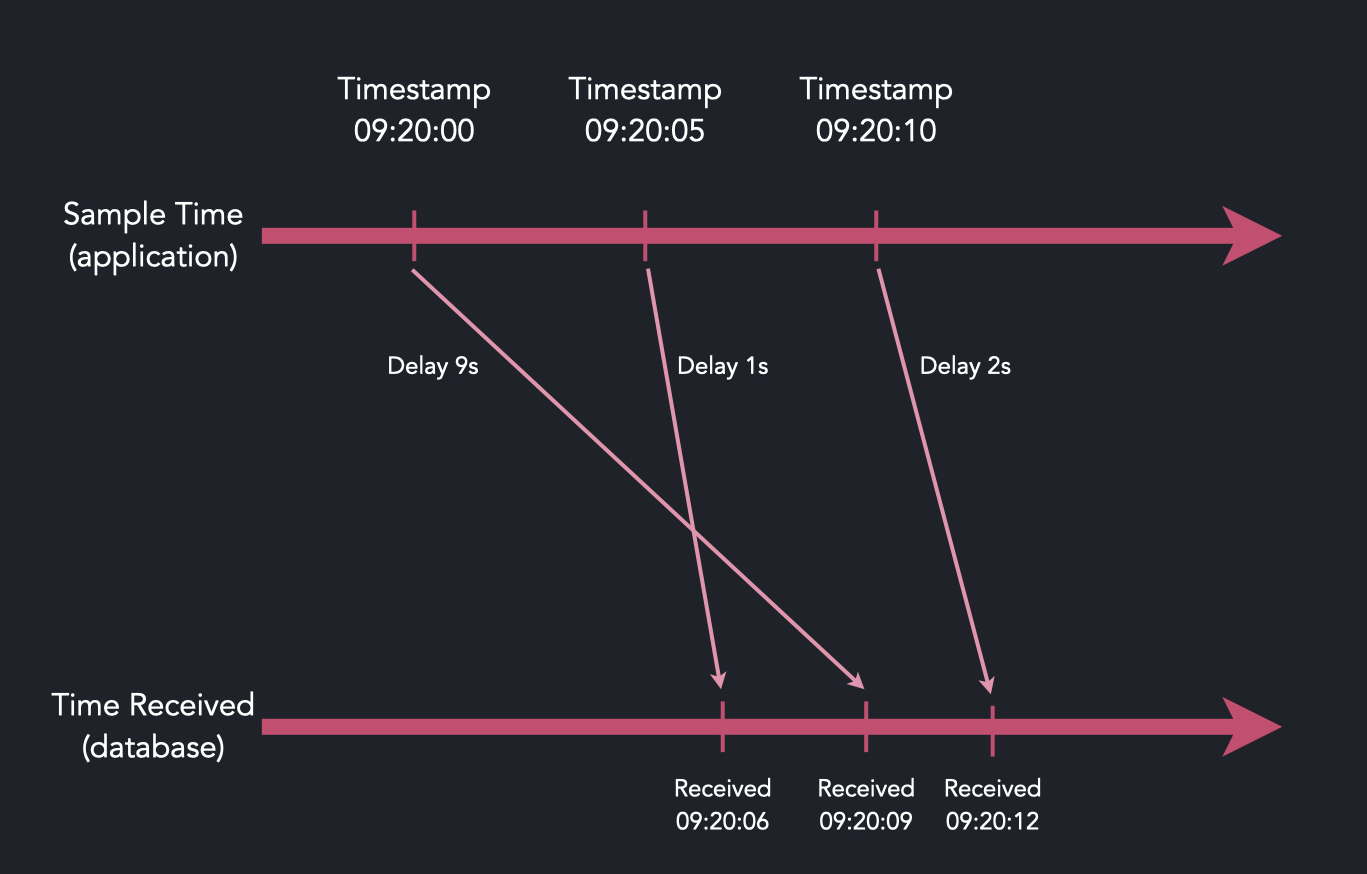
If any new timestamp value has a high probability to arrive within 10 seconds of
the previously received value, the boundary for this data is 10 seconds and we
name this commit lag or just lag.
Data received within the commit lag value is kept in memory only, and invisible from queries. Our out-of-order algorithm detects and prioritizes the data using an optimized processing path to commit later. Once committed, the data is visible for queries.
Benefits of commit lag configuration#
QuestDB stores all table data physically sorted by designated timestamp. When all data is received in a chronological order, this operation is straight-forward. If QuestDB ingests a row with a designated timestamp earlier than the latest timestamp already committed for one table, this row is out-of-order and QuestDB's engine needs to re-sort the existing data on disk. The operation to ingest O3 data is therefore costly.
For optimal ingestion performance, the number of O3 data commits should be minimized. Configuring the commit lag based on data usage is therefore a way to optimize data ingestion, by accumulating data for a set period of time, sorting the collected data in order, and committing it to memory. Although data may not be immediately visible as a result of the commit lag setting, the overall data ingestion efficiency can be improved.
Commit lag and commit timing#
Commit lag is a user configurable value. On the server level configuration, the
value is defined in milliseconds by cairo.commit.lag. Commit lag has an impact
on the timing of commit, as the value is combined with other parameters for
ILP commit strategy.
The cairo.commit.lag value is applied each time when a commit happens. As a
result, data older than the lag value will be committed and become visible.
When to change the commit lag value#
The commit lag value should be considered together with
cairo.max.uncommitted.rows as part of the
ILP commit strategy.
The default configuration for the server is as follows:
Users should modify these parameters based on any known or expected pattern for:
- The length of time by which most records are late
- The frequency of incoming records and the expected throughput
- The freshness of the data used in queries
To minimize the number of O3 data commits, if the throughput is low and timestamps are expected to be consistently delayed up to 30 seconds, the following configuration settings can be applied:
For high-throughput scenarios, a lower commit lag value combined with a larger number of uncommitted rows may be more appropriate. The following settings would assume a throughput of ten thousand records per second with a likely maximum of 1 second lateness for timestamp values:
How to configure O3 ingestion#
QuestDB provides the following O3 data ingestion configuration options; users can choose the most suitable configuration based on their specific case:
Server-wide configuration:
cairo.commit.lagin Cairo engine
Table configuration:
- Setting table parameters via SQL using SET PARAM
- Creating table with parameters via SQL using WITH
- SQL
INSERT AS SELECTwith batch size and lag: Inserting query results
Import configuration:
Out-of-order CSV import#
It is possible to set commitLag and maxUncommittedRows via REST API when
importing data via the /imp endpoint. The commitLag unit is microsecond. The
following example imports a file which contains out-of-order records. The
timestamp and partitionBy parameters must be provided for commit lag and
max uncommitted rows to have any effect: